Crypto Scams: How to Spot and Avoid Them
- 02 Sep 2024
- Crypto OG's mentioned:
- Exchanges mentioned:

As the popularity of cryptocurrency continues to grow, so does the number of scams targeting unsuspecting investors. The decentralized and often anonymous nature of cryptocurrency transactions makes it an attractive target for fraudsters. This guide will help you understand the most common types of cryptocurrency scams and how to protect yourself from falling victim to them.
High-Profile Examples of Crypto Scams
Two of the most notorious figures in the cryptocurrency world, Ruja Ignatova and Sam Bankman, orchestrated scams that left lasting scars on the crypto industry.
Ruja Ignatova, famously known as the "Cryptoqueen," was the mastermind behind the OneCoin Ponzi scheme. Promising revolutionary innovation in cryptocurrency, she defrauded millions of investors before disappearing in 2017. Her story highlights how trust and charisma can be manipulated to perpetrate massive financial fraud.
Sam Bankman, once celebrated as a crypto prodigy, founded the FTX exchange, which later collapsed in 2022. His misuse of customer funds for personal gain and high-risk investments resulted in devastating losses for investors, shaking confidence in the broader crypto market.
These examples underscore the importance of vigilance and thorough research when engaging with any cryptocurrency project or platform. Understanding their stories can help you recognize warning signs and avoid similar pitfalls.
1. Phishing Attacks
What is Phishing?
Phishing is a type of scam where attackers trick you into giving away sensitive information, such as private keys or login credentials, by pretending to be a trustworthy entity. Phishing attacks are often conducted through fake websites, emails, or social media messages that mimic legitimate platforms.
How to Avoid Phishing Scams
- Always check the URL: Before entering your login details, ensure the website URL is correct. Scammers often create fake websites with URLs that are almost identical to legitimate ones.
- Use Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Enable 2FA on all your accounts to add an extra layer of security.
- Be cautious of unsolicited messages: Never click on links or download attachments from unknown or suspicious emails or messages.
- Verify the sender: Always double-check the sender's information if you receive an email or message asking for sensitive information.

2. Ponzi and Pyramid Schemes
What are Ponzi and Pyramid Schemes?
These schemes promise high returns with little to no risk. Ponzi schemes involve paying returns to earlier investors using the capital of newer investors, while pyramid schemes require participants to recruit others in order to earn returns.
How to Spot and Avoid Ponzi and Pyramid Schemes
- Unrealistic promises: Be wary of investments that guarantee high returns with little risk. In the crypto world, if it sounds too good to be true, it probably is.
- Pressure to recruit: If an investment opportunity pressures you to recruit others to earn more, it's likely a pyramid scheme.
- Lack of transparency: Legitimate investments are transparent about their business model, team, and financials. Avoid schemes that are vague or secretive about how they generate returns.
3. Fake Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs)
What is an ICO?
An ICO is a fundraising method where new cryptocurrencies or tokens are sold to investors. While many legitimate projects use ICOs to raise capital, scammers also create fake ICOs to steal investors' money.
How to Identify and Avoid Fake ICOs
- Research the team: Legitimate projects have a transparent and experienced team. Verify the credentials of the team members and their previous work.
- Check the whitepaper: A well-written whitepaper is a sign of a legitimate project. Be cautious of poorly written, vague, or overly technical whitepapers that don't clearly explain the project's goals and use case.
- Look for community engagement: Legitimate projects often have active communities on social media and forums. Lack of community engagement or overly moderated discussions can be a red flag.
- Verify token details: Ensure the token distribution details, such as the total supply and the distribution method, are clearly outlined and make sense.
4. Rug Pulls
What is a Rug Pull?
A rug pull occurs when the developers of a cryptocurrency project suddenly withdraw all funds from the liquidity pool, leaving investors with worthless tokens. This is common in decentralized finance (DeFi) projects and newly launched tokens.
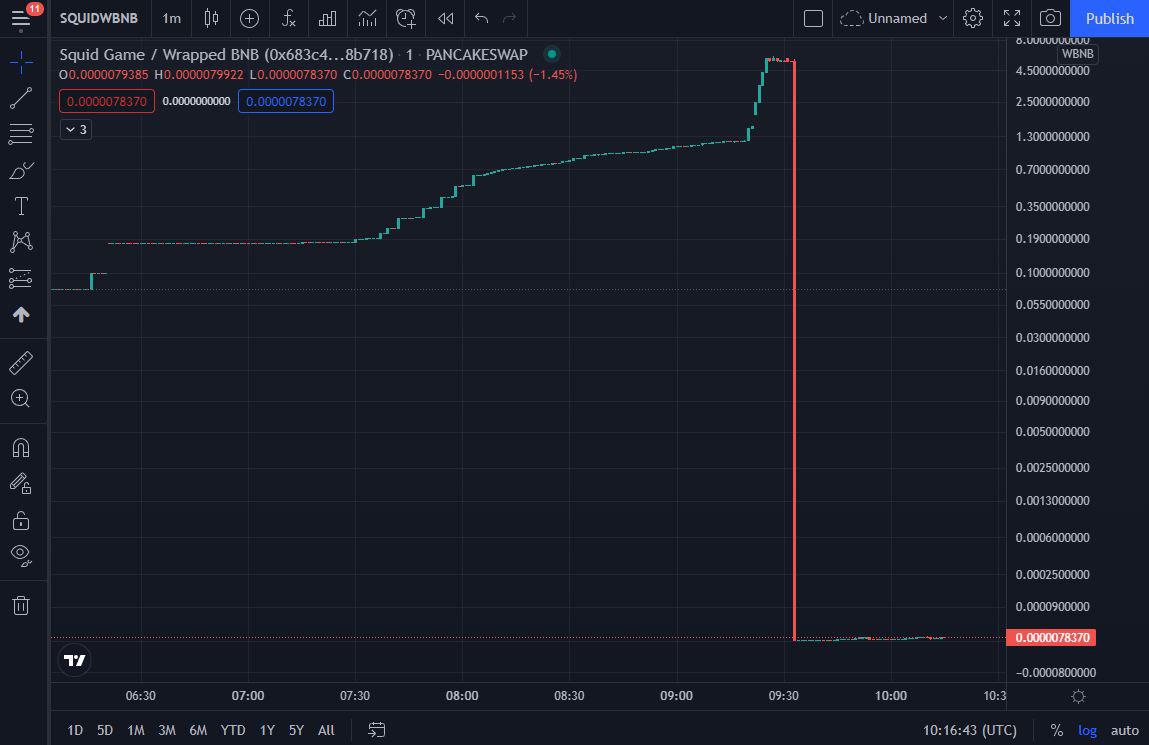
How to Avoid Rug Pulls
- Research the project: Look into the project's history, the development team, and their previous work. Anonymous or unverified teams are a red flag.
- Check the liquidity pool: Ensure the project has a locked liquidity pool, meaning the developers cannot withdraw funds suddenly.
- Look for audits: Projects that have undergone third-party audits are generally safer. Audits can help identify potential security vulnerabilities or malicious code.
5. Fake Exchanges and Wallets
What are Fake Exchanges and Wallets?
Scammers create fake cryptocurrency exchanges or wallets to steal users' funds or private keys. These platforms often look legitimate and may even offer competitive rates to lure users in.
How to Avoid Fake Exchanges and Wallets
- Use reputable exchanges: Stick to well-known and trusted exchanges like Binance, Coinbase, or KuCoin. Always verify the URL before logging in.
- Check for reviews: Before using a new exchange or wallet, check for reviews and feedback from other users. Avoid platforms with little to no online presence or negative reviews.
- Secure your funds: Store your cryptocurrency in secure wallets where you control the private keys. For more information on how to securely store your crypto, refer to our crypto wallets guide.
6. Social Media Scams
What are Social Media Scams?
Scammers use social media platforms to promote fake giveaways, impersonate influencers, or create fake profiles to trick users into sending cryptocurrency. These scams often involve promises of free crypto in exchange for a small "verification" payment.
How to Avoid Social Media Scams
- Be skeptical of giveaways: Legitimate giveaways do not require you to send funds first. Avoid any offers that ask for payment to receive a prize.
- Verify profiles: Be cautious of messages from accounts claiming to be influencers or celebrities. Check for verification marks and cross-check with their official profiles.
- Report scams: If you encounter a scam on social media, report it to the platform immediately to protect others.
7. Impersonation Scams
What are Impersonation Scams?
Scammers pose as trusted figures or companies, often using fake email addresses or social media profiles that closely resemble legitimate ones. They may claim to offer support, investment opportunities, or urgent requests for payment.

How to Avoid Impersonation Scams
- Always verify identities: If you receive a message from someone claiming to be a trusted figure, double-check their identity through official channels before taking any action.
- Contact support directly: If you're contacted by someone claiming to be from customer support, visit the official website and contact them directly instead of responding to the message.
- Be cautious with unsolicited requests: If someone contacts you out of the blue with an investment opportunity or request for payment, approach it with skepticism.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency scams are becoming increasingly sophisticated, but by staying informed and vigilant, you can protect yourself from falling victim. Always conduct thorough research before investing, use secure platforms, and be cautious of any offers that seem too good to be true. Remember, the best defense against scams is a healthy dose of skepticism and a commitment to doing your own research (DYOR).